Electrical noise properties in aging materials
L. Buisson, M. Ciccotti, L. Bellon and S. Ciliberto, Fluctuations and Noise in Materials. Edited by D. Popovic, M. Weissman and Z. Racz. Proceedings of SPIE 5469 150-164 (2004)
doi: 10.1117/12.545381
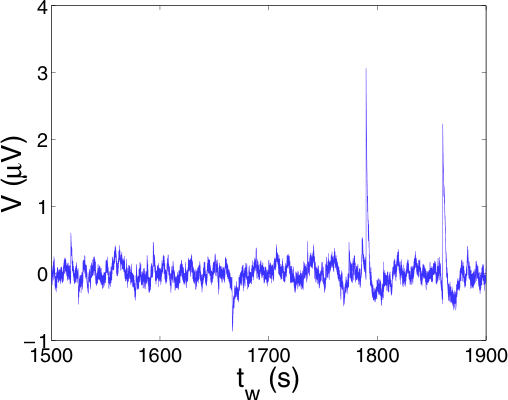
The electric thermal noise has been measured in two aging materials, a colloidal suspension (Laponite) and a polymer (polycarbonate), presenting very slow relaxation towards equilibrium. The measurements have been performed during the transition from a. fluid-like to a. solid-like state for the gel and after a. quench for the polymer. For both materials we have observed that the electric noise is characterized by a strong intermittency, which induces a large violation of the Fluctuation Dissipation Theorem (FDT) during the aging time; and may persist for several hours at low frequency. The statistics of these intermittent signals and their dependance on the quench speed for the polymer or oil sample concentration for the gel are studied. The results are in a qualitative agreement with recent models of aging, that predict an intermittent dynamics.
Proceedings of the 2nd SPIE International Symposium on Fluctuations and Noise, Maspalomas, Spain, 26-28 may 2004.
26/05/04