The corresponding .v file (with proofs) is here;
see module utas for monoids, semirings, Kleene algebras, and allegories;
and module mall for cyclic MALL (or involutive residuated lattices) and residuated lattices (without additive constants).
Section perm.
Variable A: Set.
Lemma app_app: forall (h k h' k': list A), h++k = h'++k' ->
exists l', h=h'++l' /\ k'=l'++k \/ h'=h++l' /\ k=l'++k'.
Lemma nil_app: forall (h k: list A), [] = h++k -> []=h /\ []=k.
Lemma consnil_app: forall u (h k: list A), [u] = h++k -> [u]=h /\ []=k \/ []=h /\ [u]=k.
Lemma cons_app: forall u (l h k: list A), u::l = h++k -> []=h /\ u::l=k \/ exists h', h=u::h' /\ l=h'++k.
Lemma split_select: forall (h k h' k': list A), h++k = h'++k' ->
exists l', h=h'++l' /\ k'=l'++k \/ h'=h++l' /\ k=l'++k'.
Inductive perm: relation (list A) :=
| perm_app: forall h k, perm (h++k) (k++h).
Global Instance perm_equivalence: Equivalence perm.
Infix " (=) " := perm (at level 80).
Lemma permut_cons: forall u l k, l++[u] (=) k -> u::l (=) k.
Lemma permut_app: forall h l k, l++h (=) k -> h++l (=) k.
Lemma pmor1: forall P: list A -> Prop, (forall a l, P (l++[a]) -> P (a::l)) -> Proper (perm ==> iff) P.
End perm.
Variable A: Set.
Lemma app_app: forall (h k h' k': list A), h++k = h'++k' ->
exists l', h=h'++l' /\ k'=l'++k \/ h'=h++l' /\ k=l'++k'.
Lemma nil_app: forall (h k: list A), [] = h++k -> []=h /\ []=k.
Lemma consnil_app: forall u (h k: list A), [u] = h++k -> [u]=h /\ []=k \/ []=h /\ [u]=k.
Lemma cons_app: forall u (l h k: list A), u::l = h++k -> []=h /\ u::l=k \/ exists h', h=u::h' /\ l=h'++k.
Lemma split_select: forall (h k h' k': list A), h++k = h'++k' ->
exists l', h=h'++l' /\ k'=l'++k \/ h'=h++l' /\ k=l'++k'.
Inductive perm: relation (list A) :=
| perm_app: forall h k, perm (h++k) (k++h).
Global Instance perm_equivalence: Equivalence perm.
Infix " (=) " := perm (at level 80).
Lemma permut_cons: forall u l k, l++[u] (=) k -> u::l (=) k.
Lemma permut_app: forall h l k, l++h (=) k -> h++l (=) k.
Lemma pmor1: forall P: list A -> Prop, (forall a l, P (l++[a]) -> P (a::l)) -> Proper (perm ==> iff) P.
End perm.
equality of lists, modulo cyclic permutations
X is the set of variables, it could be kept abstract
trivial typing environment
terms (formulae)
Inductive T: Set :=
| dot: T -> T -> T
| par: T -> T -> T
| one: T
| bot: T
| var: X -> T
| rav: X -> T.
| dot: T -> T -> T
| par: T -> T -> T
| one: T
| bot: T
| var: X -> T
| rav: X -> T.
notations
Notation "x $ y" := (par x y) (at level 50, left associativity): U_scope.
Notation "x ⨂ y" := (dot x y) (at level 40, left associativity): U_scope.
Notation "1" := (one): U_scope.
Notation "⊥" := (bot): U_scope.
Notation "x ⨂ y" := (dot x y) (at level 40, left associativity): U_scope.
Notation "1" := (one): U_scope.
Notation "⊥" := (bot): U_scope.
linear negation, note that it reverses arguments of tensors and pars
Fixpoint dual u :=
match u with
| a ⨂ b => dual b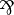 dual a
dual a
| a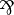 b => dual b ⨂ dual a
b => dual b ⨂ dual a
| 1 => ⊥
| ⊥ => 1
| var i => rav i
| rav i => var i
end.
match u with
| a ⨂ b => dual b
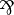 dual a
dual a| a
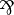 b => dual b ⨂ dual a
b => dual b ⨂ dual a| 1 => ⊥
| ⊥ => 1
| var i => rav i
| rav i => var i
end.
linear negation is involutive, and hence, injective
Lemma dual_invol: forall u, dual (dual u) = u.
Lemma dual_inj: forall u v, dual u = dual v -> u = v.
Lemma dual_inj: forall u v, dual u = dual v -> u = v.
extension of linear negation to lists, note that it reverses lists
input and output formulae (Danos-Regnier polarities)
Inductive input: T -> Prop :=
| i_rav: forall i, input (rav i)
| i_par: forall a b, input a -> input b -> input (a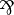 b)
b)
| i_bot: input ⊥
| i_dot_l: forall a b, input a -> output b -> input (a ⨂ b)
| i_dot_r: forall a b, output a -> input b -> input (a ⨂ b)
with output: T -> Prop :=
| o_var: forall i, output (var i)
| o_dot: forall a b, output a -> output b -> output (a ⨂ b)
| o_one: output 1
| o_par_l: forall a b, output a -> input b -> output (a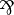 b)
b)
| o_par_r: forall a b, input a -> output b -> output (a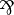 b)
b)
.
| i_rav: forall i, input (rav i)
| i_par: forall a b, input a -> input b -> input (a
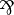 b)
b)| i_bot: input ⊥
| i_dot_l: forall a b, input a -> output b -> input (a ⨂ b)
| i_dot_r: forall a b, output a -> input b -> input (a ⨂ b)
with output: T -> Prop :=
| o_var: forall i, output (var i)
| o_dot: forall a b, output a -> output b -> output (a ⨂ b)
| o_one: output 1
| o_par_l: forall a b, output a -> input b -> output (a
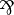 b)
b)| o_par_r: forall a b, input a -> output b -> output (a
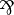 b)
b).
input lists
Inductive linput: list T -> Prop :=
| i_nil: linput nil
| i_cons: forall i l, input i -> linput l -> linput (i::l).
| i_nil: linput nil
| i_cons: forall i l, input i -> linput l -> linput (i::l).
linear negation goes from input to output formulae, and vice-versa
Lemma dual_input: forall u, input u -> output (dual u)
with dual_output: forall u, output u -> input (dual u).
with dual_output: forall u, output u -> input (dual u).
lemmas about input lists
Lemma i_app_inv: forall h k, linput (h++k) -> linput h /\ linput k.
Lemma i_app: forall h k, linput h -> linput k -> linput (h++k).
Lemma i_app: forall h k, linput h -> linput k -> linput (h++k).
a formula cannot be both input and output (not used in the sequel)
I is the set of pretypes, s and t give the typing environment (source and target)
MLL typing judgement, for formulae, and lists
Inductive typed: I -> I -> T -> Prop :=
| t_var: forall x, typed (s x) (t x) (var x)
| t_rav: forall x, typed (t x) (s x) (rav x)
| t_one: forall n, typed n n 1
| t_bot: forall n, typed n n ⊥
| t_dot: forall n m o u v, typed n m u -> typed m o v -> typed n o (u ⨂ v)
| t_par: forall n m o u v, typed n m u -> typed m o v -> typed n o (u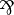 v).
v).
Inductive ltyped: I -> I -> list T -> Prop :=
| t_nil: forall n, ltyped n n []
| t_cons: forall n m p l u, typed n m u -> ltyped m p l -> ltyped n p (u::l).
Lemma t_app: forall l l' n m p, ltyped n m l -> ltyped m p l' -> ltyped n p (l++l').
Lemma t_app_inv: forall l l' n p, ltyped n p (l++l') -> exists2 m, ltyped n m l & ltyped m p l'.
| t_var: forall x, typed (s x) (t x) (var x)
| t_rav: forall x, typed (t x) (s x) (rav x)
| t_one: forall n, typed n n 1
| t_bot: forall n, typed n n ⊥
| t_dot: forall n m o u v, typed n m u -> typed m o v -> typed n o (u ⨂ v)
| t_par: forall n m o u v, typed n m u -> typed m o v -> typed n o (u
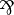 v).
v).Inductive ltyped: I -> I -> list T -> Prop :=
| t_nil: forall n, ltyped n n []
| t_cons: forall n m p l u, typed n m u -> ltyped m p l -> ltyped n p (u::l).
Lemma t_app: forall l l' n m p, ltyped n m l -> ltyped m p l' -> ltyped n p (l++l').
Lemma t_app_inv: forall l l' n p, ltyped n p (l++l') -> exists2 m, ltyped n m l & ltyped m p l'.
linear negation mirrors types
Lemma t_dual: forall u n m, typed n m u -> typed m n (dual u).
Lemma t_ldual: forall l n m, ltyped n m l -> ltyped m n (ldual l).
Lemma t_ldual: forall l n m, ltyped n m l -> ltyped m n (ldual l).
injectivity property of typing derivations
Lemma typed_inj: forall u n m, typed n m u -> forall n' m', typed n' m' u -> n=n' /\ m=m' \/ n=m /\ n'=m'.
Lemma ltyped_inj: forall l n m, ltyped n m l -> forall n' m', ltyped n' m' l -> n=n' /\ m=m' \/ n=m /\ n'=m'.
Lemma ltyped_inj: forall l n m, ltyped n m l -> forall n' m', ltyped n' m' l -> n=n' /\ m=m' \/ n=m /\ n'=m'.
typed sequent system for cyclic MLL
Inductive seq: I -> list T -> Prop :=
| seq_ax: forall i, seq (t i) [rav i; var i]
| seq_one: forall n, seq n [1]
| seq_bot: forall l n, seq n l -> seq n (⊥::l)
| seq_dot: forall a b h l n, seq n (l++[a]) -> seq n (b::h) -> seq n (l++a ⨂ b::h)
| seq_par: forall a b l n, seq n (a::b::l) -> seq n (a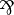 b::l)
b::l)
| seq_rot: forall a l n m, typed n m a -> seq m (l++[a]) -> seq n (a::l).
| seq_ax: forall i, seq (t i) [rav i; var i]
| seq_one: forall n, seq n [1]
| seq_bot: forall l n, seq n l -> seq n (⊥::l)
| seq_dot: forall a b h l n, seq n (l++[a]) -> seq n (b::h) -> seq n (l++a ⨂ b::h)
| seq_par: forall a b l n, seq n (a::b::l) -> seq n (a
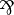 b::l)
b::l)| seq_rot: forall a l n m, typed n m a -> seq m (l++[a]) -> seq n (a::l).
sanity check: derivable sequents have square types
admissible variant of rule seq_rot: rotate the sequent to an arbitrary position
admissible variant of rule seq_dot
Lemma seq_dot': forall a b h l n m, typed n m a -> seq n (a::l) -> seq m (b::h) -> seq n (a ⨂ b::h++l).
the sequent system is "reflexive"
input sequents cannot be proved
cut admissibility (not proved here, not used in the sequel)
untyped means typed in the trivial environment ;
useq mean derivable in the untyped setting ;
terms and lists are always untyped
Lemma always_untyped: forall u, typed ttt ttt tt tt u.
Lemma always_luntyped: forall l, ltyped ttt ttt tt tt l.
Section erase.
Variable I: Set.
Variables s t: X -> I.
Notation ltyped := (ltyped s t).
Notation typed := (typed s t).
Notation seq := (seq s t).
Lemma always_luntyped: forall l, ltyped ttt ttt tt tt l.
Section erase.
Variable I: Set.
Variables s t: X -> I.
Notation ltyped := (ltyped s t).
Notation typed := (typed s t).
Notation seq := (seq s t).
key lemma: types of derivable sequents are squares
untyping theorem for cyclic MLL
typed derivable sequents are untyped derivable
terms
Inductive T: Set :=
| dot: T -> T -> T
| ldv: T -> T -> T
| rdv: T -> T -> T
| one: T
| var: X -> T.
| dot: T -> T -> T
| ldv: T -> T -> T
| rdv: T -> T -> T
| one: T
| var: X -> T.
notations
Notation "x * y" := (dot x y) (at level 40, left associativity): V_scope.
Notation "x / y" := (rdv x y) (at level 40, left associativity): V_scope.
Notation "x \ y" := (ldv x y) (at level 40, left associativity): V_scope.
Notation "1" := (one): V_scope.
Notation "x / y" := (rdv x y) (at level 40, left associativity): V_scope.
Notation "x \ y" := (ldv x y) (at level 40, left associativity): V_scope.
Notation "1" := (one): V_scope.
encoding of IMLL formulae into MLL formulae
Fixpoint to_MLL (u: T): MLL.T :=
match u with
| a * b => to_MLL a ⨂ to_MLL b
| a \ b => dual (to_MLL a)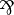 to_MLL b
to_MLL b
| a / b => to_MLL a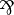 dual (to_MLL b)
dual (to_MLL b)
| 1 => MLL.one
| var x => MLL.var x
end.
match u with
| a * b => to_MLL a ⨂ to_MLL b
| a \ b => dual (to_MLL a)
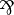 to_MLL b
to_MLL b| a / b => to_MLL a
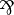 dual (to_MLL b)
dual (to_MLL b)| 1 => MLL.one
| var x => MLL.var x
end.
extension to lists of formulae (warning: this function already applies the linear negation)
encoding of a concatenation
the encoding produces output formulae
the encoding of list produces lists of input formulae
inversion lemmas, to reason about cyclic permutations
Lemma lto_MLL_app_inv: forall q l h,
l++h = lto_MLL q -> exists l', exists h', q=h'++l' /\ lto_MLL l' = l /\ lto_MLL h' = h.
Lemma lto_MLL_cons_inv: forall q u h,
u::h = lto_MLL q -> exists u', exists h', q=h'++[u'] /\ to_MLL u' = MLL.dual u /\ lto_MLL h' = h.
l++h = lto_MLL q -> exists l', exists h', q=h'++l' /\ lto_MLL l' = l /\ lto_MLL h' = h.
Lemma lto_MLL_cons_inv: forall q u h,
u::h = lto_MLL q -> exists u', exists h', q=h'++[u'] /\ to_MLL u' = MLL.dual u /\ lto_MLL h' = h.
inversion of the encoding
I is the set of pretypes, s and t give the typing environment (source and target)
IMLL typing judgements, for formulae and lists
Inductive typed: I -> I -> T -> Prop :=
| t_var: forall x, typed (s x) (t x) (var x)
| t_one: forall n, typed n n 1
| t_dot: forall n m o u v, typed n m u -> typed m o v -> typed n o (u * v)
| t_ldv: forall n m o u v, typed m n u -> typed m o v -> typed n o (u \ v)
| t_rdv: forall n m o u v, typed o m u -> typed n m v -> typed n o (v / u).
Inductive ltyped: I -> I -> list T -> Prop :=
| t_nil: forall n, ltyped n n []
| t_cons: forall n m p l u, typed n m u -> ltyped m p l -> ltyped n p (u::l).
Lemma t_app: forall l l' n m p, ltyped n m l -> ltyped m p l' -> ltyped n p (l++l').
Lemma t_app_inv: forall l l' n p, ltyped n p (l++l') -> exists2 m, ltyped n m l & ltyped m p l'.
| t_var: forall x, typed (s x) (t x) (var x)
| t_one: forall n, typed n n 1
| t_dot: forall n m o u v, typed n m u -> typed m o v -> typed n o (u * v)
| t_ldv: forall n m o u v, typed m n u -> typed m o v -> typed n o (u \ v)
| t_rdv: forall n m o u v, typed o m u -> typed n m v -> typed n o (v / u).
Inductive ltyped: I -> I -> list T -> Prop :=
| t_nil: forall n, ltyped n n []
| t_cons: forall n m p l u, typed n m u -> ltyped m p l -> ltyped n p (u::l).
Lemma t_app: forall l l' n m p, ltyped n m l -> ltyped m p l' -> ltyped n p (l++l').
Lemma t_app_inv: forall l l' n p, ltyped n p (l++l') -> exists2 m, ltyped n m l & ltyped m p l'.
injectivity property of types
Lemma typed_inj: forall u n m, typed n m u -> forall n' m', typed n' m' u -> n=n' /\ m=m' \/ n=m /\ n'=m'.
Lemma ltyped_inj: forall l n m, ltyped n m l -> forall n' m', ltyped n' m' l -> n=n' /\ m=m' \/ n=m /\ n'=m'.
Lemma ltyped_inj: forall l n m, ltyped n m l -> forall n' m', ltyped n' m' l -> n=n' /\ m=m' \/ n=m /\ n'=m'.
the encoding preserve types
Lemma typed_to_MLL: forall u n m, typed n m u -> MLL.typed s t n m (to_MLL u).
Lemma ltyped_to_MLL: forall l n m, ltyped n m l -> MLL.ltyped s t m n (lto_MLL l).
Lemma to_MLL_typed: forall u n m, MLL.typed s t n m (to_MLL u) -> typed n m u.
Lemma to_MLL_ltyped: forall l n m, MLL.ltyped s t n m (lto_MLL l) -> ltyped m n l.
Lemma ltyped_to_MLL: forall l n m, ltyped n m l -> MLL.ltyped s t m n (lto_MLL l).
Lemma to_MLL_typed: forall u n m, MLL.typed s t n m (to_MLL u) -> typed n m u.
Lemma to_MLL_ltyped: forall l n m, MLL.ltyped s t n m (lto_MLL l) -> ltyped m n l.
sequent proof system for residuated monoids
Inductive leq: I -> I -> list T -> T -> Prop :=
| leq_var: forall i, leq (s i) (t i) [var i] (var i)
| one_intro: forall n, leq n n [] 1
| one_elim: forall n m l l' u, leq n m (l++l') u -> leq n m (l++1::l') u
| dot_intro: forall n m p l l' u u', leq n m l u -> leq m p l' u' -> leq n p (l++l') (u * u')
| dot_elim: forall n m l v w l' u, leq n m (l++v::w::l') u -> leq n m (l++(v * w)::l') u
| rdv_intro: forall n m p u v l, typed p m v -> leq n m (l++[v]) u -> leq n p l (u / v)
| rdv_elim: forall n m p q l k v w l' u, ltyped m q l' ->
leq n m k v -> leq p q (l++w::l') u -> leq p q (l++(w / v)::k++l') u
| ldv_intro: forall n m p u v l, typed n p v -> leq n m (v::l) u -> leq p m l (v \ u)
| ldv_elim: forall n m p q l k v w l' u, ltyped p m l ->
leq m n k v -> leq p q (l++w::l') u -> leq p q (l++k++(v \ w)::l') u.
| leq_var: forall i, leq (s i) (t i) [var i] (var i)
| one_intro: forall n, leq n n [] 1
| one_elim: forall n m l l' u, leq n m (l++l') u -> leq n m (l++1::l') u
| dot_intro: forall n m p l l' u u', leq n m l u -> leq m p l' u' -> leq n p (l++l') (u * u')
| dot_elim: forall n m l v w l' u, leq n m (l++v::w::l') u -> leq n m (l++(v * w)::l') u
| rdv_intro: forall n m p u v l, typed p m v -> leq n m (l++[v]) u -> leq n p l (u / v)
| rdv_elim: forall n m p q l k v w l' u, ltyped m q l' ->
leq n m k v -> leq p q (l++w::l') u -> leq p q (l++(w / v)::k++l') u
| ldv_intro: forall n m p u v l, typed n p v -> leq n m (v::l) u -> leq p m l (v \ u)
| ldv_elim: forall n m p q l k v w l' u, ltyped p m l ->
leq m n k v -> leq p q (l++w::l') u -> leq p q (l++k++(v \ w)::l') u.
sanity check: derivable sequents are correctly typed
"one output, several input" cyclic MLL derivable sequents yield derivable IMLL sequents
(we start from an untyped sequent for commodity, so that we do not have to bother about
types when applying induction hypotheses)
Theorem uMLL_to_IMLL: forall n m l u, ltyped n m l -> typed n m u ->
useq (to_MLL u::lto_MLL l) -> leq n m l u.
End types.
useq (to_MLL u::lto_MLL l) -> leq n m l u.
End types.
untyped means typed in the trivial environment ;
uleq mean derivable in the untyped setting ;
Notation untyped u := (typed ttt ttt _ _ u).
Notation uleq := (leq ttt ttt tt tt).
Lemma always_untyped: forall u, typed ttt ttt tt tt u.
Lemma always_luntyped: forall l, ltyped ttt ttt tt tt l.
Notation uleq := (leq ttt ttt tt tt).
Lemma always_untyped: forall u, typed ttt ttt tt tt u.
Lemma always_luntyped: forall l, ltyped ttt ttt tt tt l.
non commutative IMLL derivable sequents yield cyclic MLL derivable sequents ;
it suffices to prove it for the untyped setting
Theorem uIMLL_to_uMLL: forall l u, uleq l u -> useq (to_MLL u::lto_MLL l).
Section erase.
Variable I: Set.
Variables s t: X -> I.
Notation ltyped := (ltyped s t).
Notation typed := (typed s t).
Notation leq := (leq s t).
Section erase.
Variable I: Set.
Variables s t: X -> I.
Notation ltyped := (ltyped s t).
Notation typed := (typed s t).
Notation leq := (leq s t).
untyping theorem for residuated monoids (non-commutative IMLL)
typed derivable sequents are untyped derivable (straightforward)
typed conversions between IMLL and MLL
Theorem IMLL_to_MLL: forall l u n m, leq n m l u -> seq s t n (to_MLL u::lto_MLL l).
Theorem MLL_to_IMLL: forall l u n m, ltyped n m l -> typed n m u -> seq s t n (to_MLL u::lto_MLL l) -> leq n m l u.
End erase.
End IMLL.
Theorem MLL_to_IMLL: forall l u n m, ltyped n m l -> typed n m u -> seq s t n (to_MLL u::lto_MLL l) -> leq n m l u.
End erase.
End IMLL.
This page has been generated by coqdoc