Our article is available to read at ChemElectroChem.
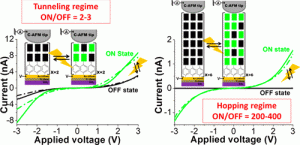
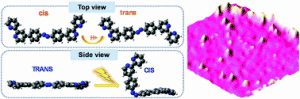
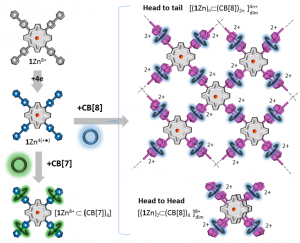
 CF3-substituted porphyrins have attracted increasing interest over the past decade. However, the number of examples reported in the literature remains quite limited and much remains to be done to understand the properties and reactivity of these molecules. We are now reporting on the synthesis of a series of free base porphyrins incorporating one, two and three CF3 substituents, including the 5,10,15-tris(CF3) substituted porphyrin which has never been described before. We have also carried out detailed electrochemical and spectroscopic analyses aiming at assessing the electron-withdrawing properties of the CF3 substituents compared to the widely used C6F5. Our studies led us to propose an interpretation of the quite unusual electrochemical signature of these molecules featuring three successive one-electron reduction waves.
CF3-substituted porphyrins have attracted increasing interest over the past decade. However, the number of examples reported in the literature remains quite limited and much remains to be done to understand the properties and reactivity of these molecules. We are now reporting on the synthesis of a series of free base porphyrins incorporating one, two and three CF3 substituents, including the 5,10,15-tris(CF3) substituted porphyrin which has never been described before. We have also carried out detailed electrochemical and spectroscopic analyses aiming at assessing the electron-withdrawing properties of the CF3 substituents compared to the widely used C6F5. Our studies led us to propose an interpretation of the quite unusual electrochemical signature of these molecules featuring three successive one-electron reduction waves.