Our very collaborative work on using generalized coordination numbers for understanding and designing active sites for alcohol dehydrogenation reactions has finally been published in J. Phys. Chem. C.
Understanding electrified interfaces
The comment I co-authored with Zhi Wei Seh from A*STAR in Nature Reviews Materials is now online! – We highlight the challenges and necessities for a better characterization and understanding of electrified interfaces. This is an important step towards a more rational design of electrocatalysts.
NatRevMatter(Dis)Similarities of adsorption of diverse functional groups over alumina and hematite depending on the surface state
It took some time – but we finally present the full comparison adsorption of various functional groups on hematite and alumina as a result of our collaboration with Total.
rank-Greville: recursive pseudo-inverse solver exploiting rank deficiency
Finally, the mathematical article of Ruben Staub is published! – If you are interested in this work, check out the GitHub page as well.
What does graphitic carbon nitride really look like?
We have published our last paper on carbon nitrides (here melon, g-C6N9H3) in PCCP. It nicely finishes our series on these materials.
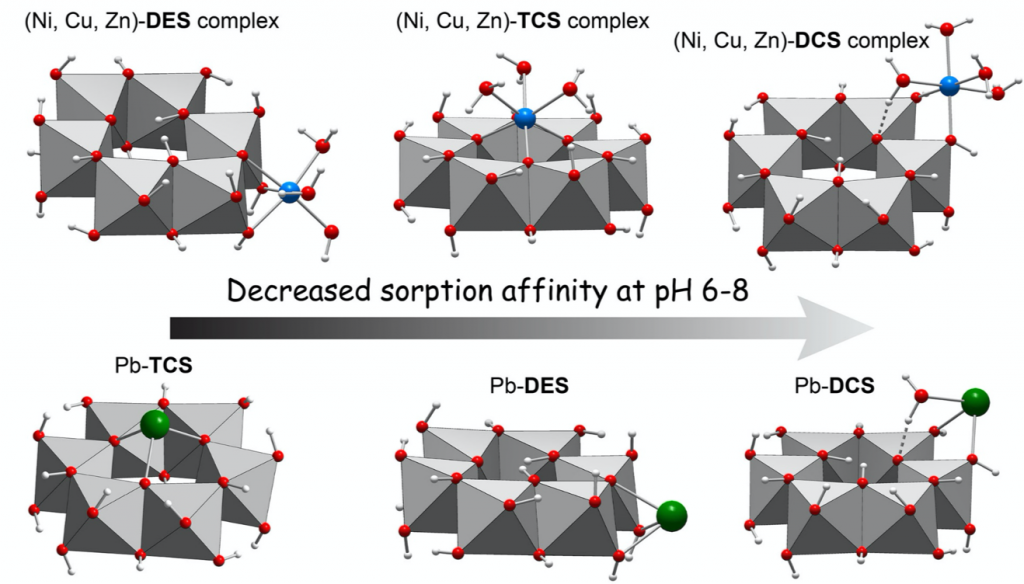
Metal Ion adsorption on Birnessite (d-MnO2)
The collaboration with Alain Manceau continues! – In our article we have gained insights that is complementary to experiments regarding the adsorption and thus incorporation of metal ions on birnessite.
Hydroxide-Induced Degradation of Olefin Metathesis Catalysts: A Challenge for Metathesis in Alkaline Media
The wonderful collaboration with Deryn Fogg from the University of Ottawa has led to insightful work on the deactivation of a typical olefin metathesis catalyst. Daniel Walden did a great computational job.
As a follow-up and with the contribution of Joshua Sims, we are very happy to announce the publication of “The Impact of Water on Ru-Catalyzed Olefin Metathesis: Potent Deactivating Effects Even at Low Water Concentrations“, once again in ACS Catalysis.
Electrolysis of a Lignin model compound
As part of our collaboration H2Lignin with A. Caravaca from IRCELyon, we have published a study on 2-phenoxyethanol electrolysis, leading to the generation of H2. In analogy to alcohol electro-oxidation, the C-C bonds are extremely hard to break, shedding shadows over the prospects of lignin electrolysis at low temperatures.
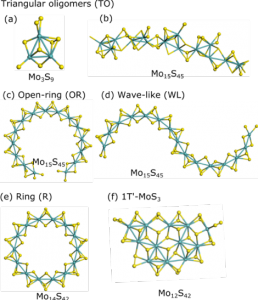
The nature of MoS3
In our recent work in collaboration with IFP Energies nouvelles we have investigated the atomic structure of amorphous MoS3. Several competing structures have been identified. – We have also evidenced an intriguing ring-structure that is among the most stable arrangements of nano-MoS3.
Solvation Free Energies and Adsorption Energies at the Metal/Water Interface
After quite some time of fiddling, I am very happy (and a bit proud) to announce that the result of our collaborative work on the use of our force field GAL17 in combination with alchemical free energy methods has been published in JCTC. The associated software, SolvHybrid, is now available on GitHub, although for now only the trunk (or our inhouse modified) version of Sander is able to perform the corresponding simulations. This work would not have been possible without the constant energy of Paul Clabaut; he has really driven this development!