M. Vial, L. Bellon and R. H. Hernandez, Experiments in Fluids 37 168-176 (2004)
doi: 10.1007/s00348-004-0796-0
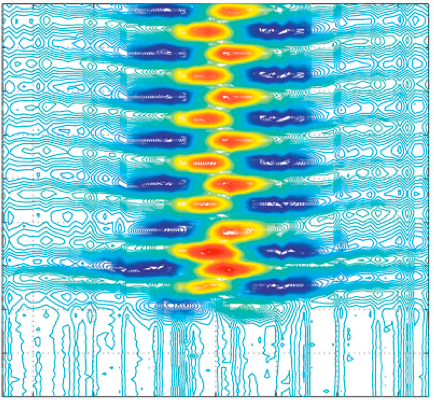
We report experimental results of the forced wake of a thin symmetric flat plate, placed parallel to an uniform air stream, in the range of thickness-based Reynolds number 50< Re (e)<200. External wake forcing was introduced by small harmonic oscillations of a moving flap, placed at the trailing-edge of the flat plate. When the flap remains in a fixed horizontal position, the mean velocity profiles obtained by hot wire measurements, for different Reynolds numbers, are self similar. In the presence of harmonic forcing, within a certain range of the forcing frequency, the mean velocity profiles change and coherent structures are formed in the wake. Two independent flow-type resonances were observed: (i) when the inverse of the forcing frequency matches the flight time of the fluid particles along the flap. (ii) when the forcing frequency of the flap equals one half of the vortex shedding frequency of the flat plate and flap system. Implications of the two observed resonances on the wake structure are important. The first resonance (i) is associated to a wide but less intense (energy fluctuations) wake flow and the second resonance (ii) generates a thin but intense resultant wake flow.