C. Devailly, J. Laurent, A. Steinberger, L. Bellon, S. Ciliberto, EPL 106, 54005 (2014)
doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/106/54005
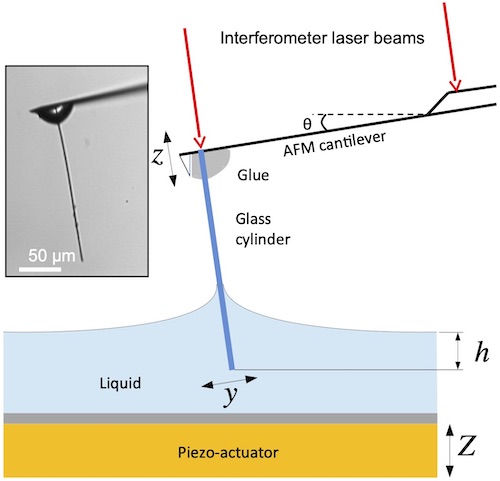
We analyze the advantages and drawbacks of a method which measures the viscosity of liquids at microscales, using a thin glass fiber fixed on the tip of a cantilever of an ultra-low-noise Atomic Force Microscope (AFM). When the fiber is dipped into a liquid, the dissipation of the cantilever-fiber system, which is linked to the liquid viscosity, can be computed from the power spectral density of the thermal fluctuations of the cantilever deflection. The high sensitivity of the AFM allows us to show the existence and to develop a model of the coupling between the dynamics of the fiber and that of the cantilever. This model, which accurately fits the experimental data, gives also more insights into the dynamics of coupled microdevices in a viscous environment.