R. H. Hernandez, M. Vial, L. Bellon and C. Baudet, in Instabilities and Nonequilibrium Structures IX, O. Descalzi, J. Martínez, S. Rica (Eds.), Kluwer Academic Publishers. Series: Nonlinear Phenomena and Complex Systems 9 195-205 (2004)
ISBN: 978-1-4020-1950-0
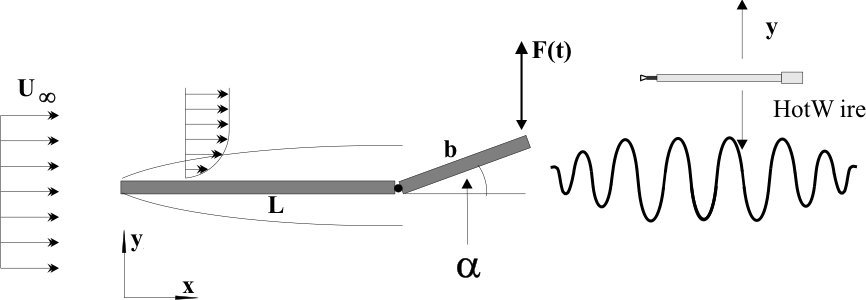
We report experimental measurements of the wake behavior of a thin flat plate submitted to an external harmonic forcing. Two slightly different configurations are examined. Classical hot wire measurements of the velocity field downstream the plate and sound scattering experiments of the near wake demonstrates that the flat plate wake displays a kind of inertial resonance when the inverse of the forcing frequency matches the flying time of fluid particles along the moving part of the plate.
Proceedings of the Ninth International Workshop on Instabilities and Nonequilibrium Structures, Viña del Mar, Chile, December 2001.