Pierdomenico Paolino, PhD Thesis, École Normale Supérieure de Lyon (2008)
hal: tel-00423692
En microscopie à force atomique (AFM), l’étude des échantillons est réalisée à l’aide d’une pointe montée sur un microlevier. Le coeur de la technique est la mesure de la force d’interaction pointe-surface, directement proportionnelle à la déflexion du levier. Plus généralement, la compréhension profonde des propriétés mécaniques des microstructures joue un rôle significatif dans le développement des microsystèmes électromécaniques (MEMS), ou encore de capteurs chimiques ou biologiques miniatures.
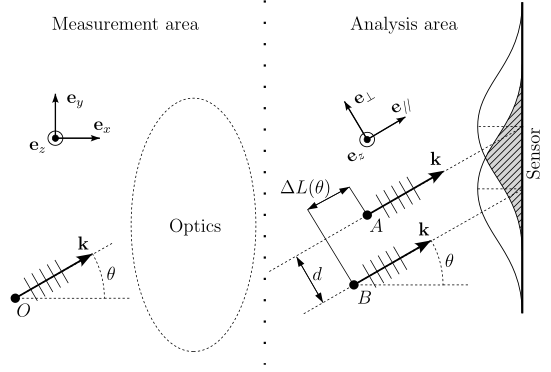
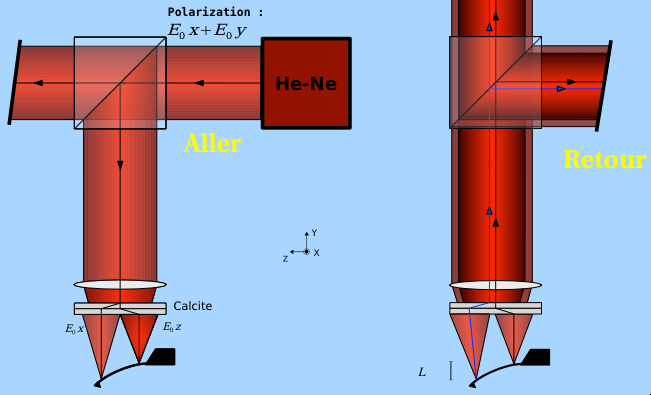
Au delà du dispositif traditionnel de mesure de déflexion angulaire, nous avons conçu et réalisé un AFM avec une détection interférométrique différentielle (entre la base encastrée et l’extrémité libre du levier). La résolution ultime est de 10-14 m/Hz1/2, la mesure est de plus intrinsèquement calibrée, indifférente aux dérives thermiques lentes et sans limitation de la plage d’amplitude de la déflexion.
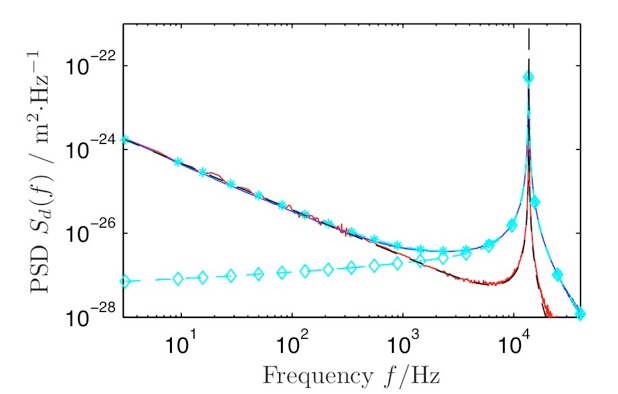
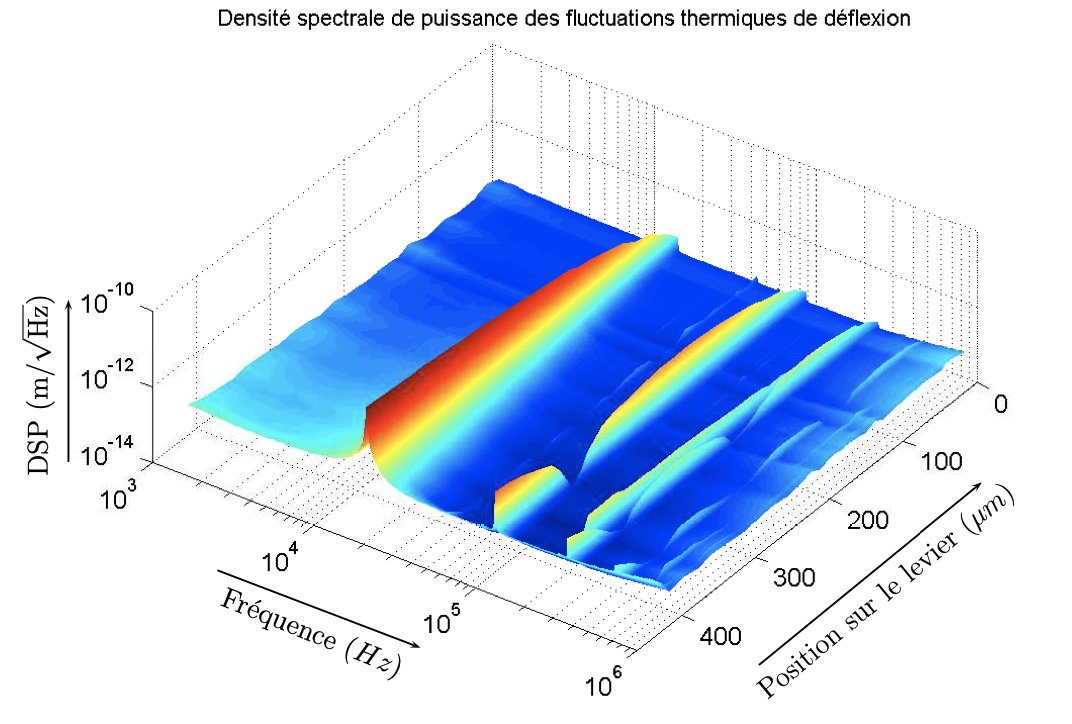
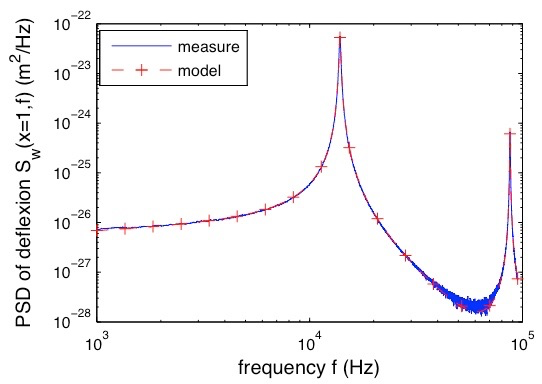
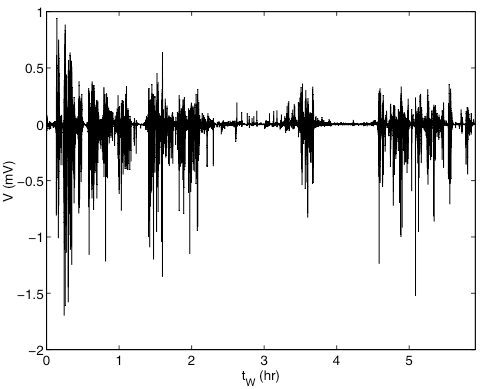
Grâce à notre dispositif, nous mesurons le bruit thermique le long du levier. Une reconstruction de la forme spatiale des quatre premiers modes propres en flexion révèle un excellent accord avec le modèle de poutre de Euler-Bernoulli. Un ajustement simultané sur les quatre résonances thermiquement excitées est réalisé à l’aide d’un seul paramètre libre : la raideur du levier, qui est ainsi mesurée avec une grande précision et robustesse.
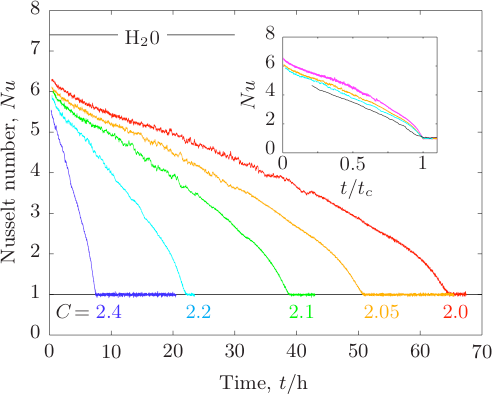
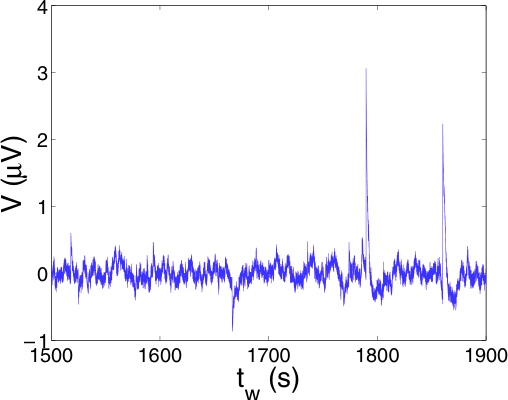
Les fluctuations thermiques de déflexion à basse fréquence démontrent qu’un modèle d’oscillateur harmonique avec dissipation visqueuse n’est plus pertinent hors résonance. De plus, on observe des différences substantielles entre les leviers avec et sans revêtement métallique. Pour ces derniers, l’approche hydrodynamique de Sader rend compte fidèlement du comportement des fluctuations en dessous de la résonance dans l’air. La présence du revêtement introduit une deuxième source de dissipation : la viscoélasticité. Elle se manifeste comme un bruit en 1/f à basse fréquence. L’utilisation du Théorème Fluctuation-Dissipation (TFD) et des relations de Kramers-Kronig permettent une caractérisation complète de la réponse du levier à l’aide des spectres de fluctuations. Une estimation quantitative de la viscoélasticité et de sa dépendance en fréquence est notamment obtenue.
Download pdf