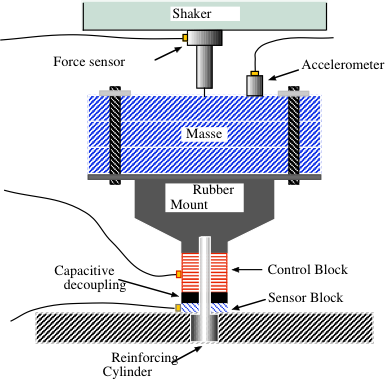
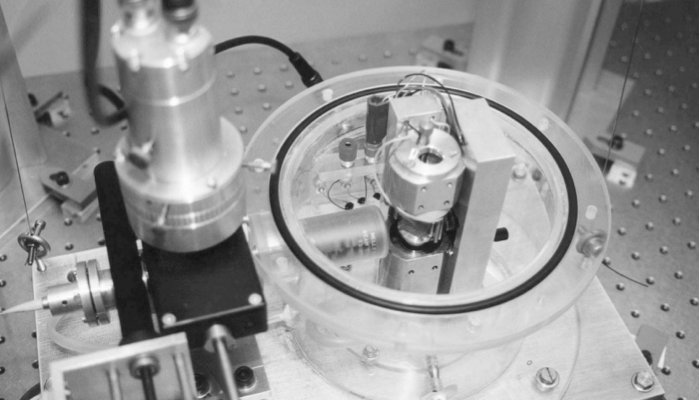
L. Bellon, Thèse de L’École Normale Supérieure de Lyon, 2001
oai: tel.archives-ouvertes.fr:tel-00003649_v1
Abstract
This thesis presents an experimental study of aging in glassy material, aiming at testing recent theoretical approaches of the subject. In a first chapter, we introduce these new concepts : based on the analogy between spin glasses and structural glasses, they define the effective temperature Teff of these weakly out of equilibrium systems. This new observable is measured with the fluctuation-dissipation ratio of such a system.
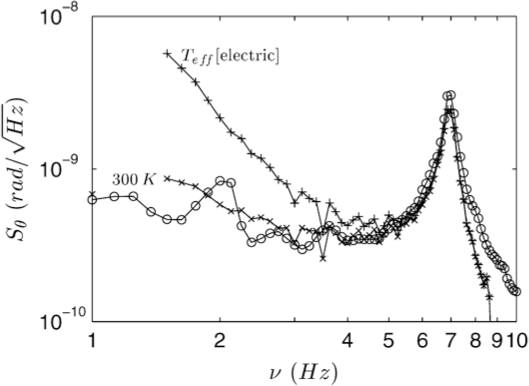
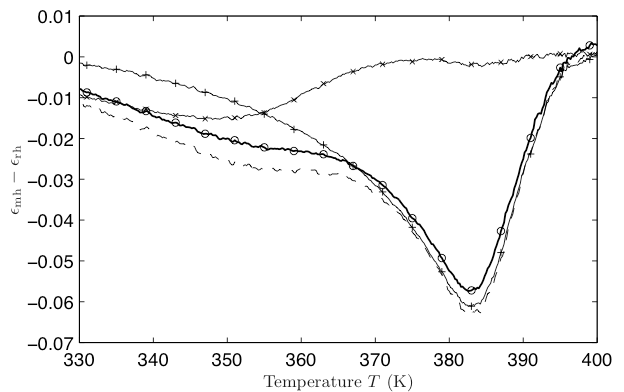
The second chapter is dedicated to the study of the rejuvenation-memory effect in a polymer (poly(methyl methacrylate) or PMMA). Based on experiments on spin glasses, this work proves a strong analogy on fine effects in the behavior of these 2 different systems. Their common properties are theoretically described in the frame of a hierarchical energy landscape. This analogy makes PMMA a good candidate for a study of the fluctuation dissipation ratio, introduced in a third chapter. Our approach, based on the measurement of electric properties, is carefully analyzed to accurately estimate error bars. We demonstrate this way that we must improve our signal to noise ratio before drawing any conclusion.
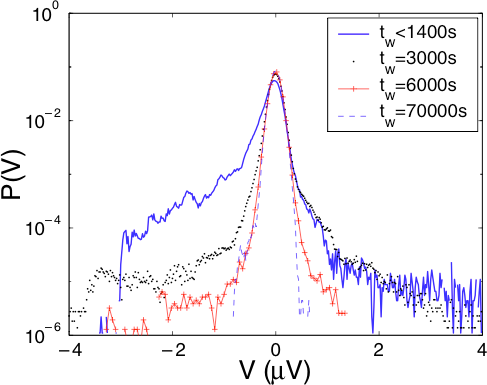
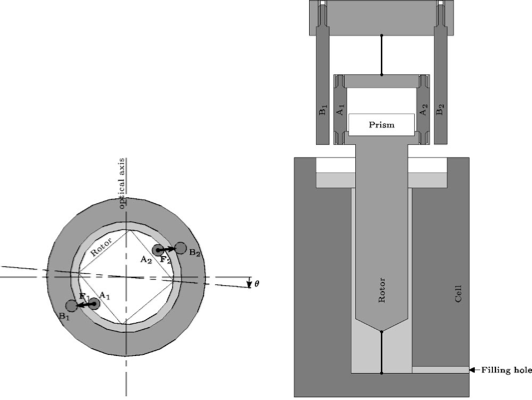
In the last two chapters, we study a colloidal glass : Laponite. The measurement of Teff, using experimental protocol of chapter 3, proves this time a clear violation of the fluctuation dissipation theorem, in agreement with recent theories on aging. To check the intrinsic character of this property, we eventually propose a second determination via a rheologic study of this material. Un ultra-sensitive rheometer is set up, and preliminary results are presented.
Keywords: aging, glass, rejuvenation-memory effect, fluctuation dissipation theorem, out of equilibrium systems, PMMA, Laponite.
Jury:
- -Bernard Castaing,
- -Sergio Ciliberto – Directeur de thèse
- -Jean-Pierre Hansen – Président du jury
- -Marc Mézard – Rapporteur
- -Gérard Vigier
- -Éric Vincent – Rapporteur
Download PDF