Variables
A variable in Python is a pointer to some content.
Address
Technically, a variable in Python is a pointer, and it contains a memory address to an allocated memory zone containing an object.
x = 42
id(x)
139907129622096
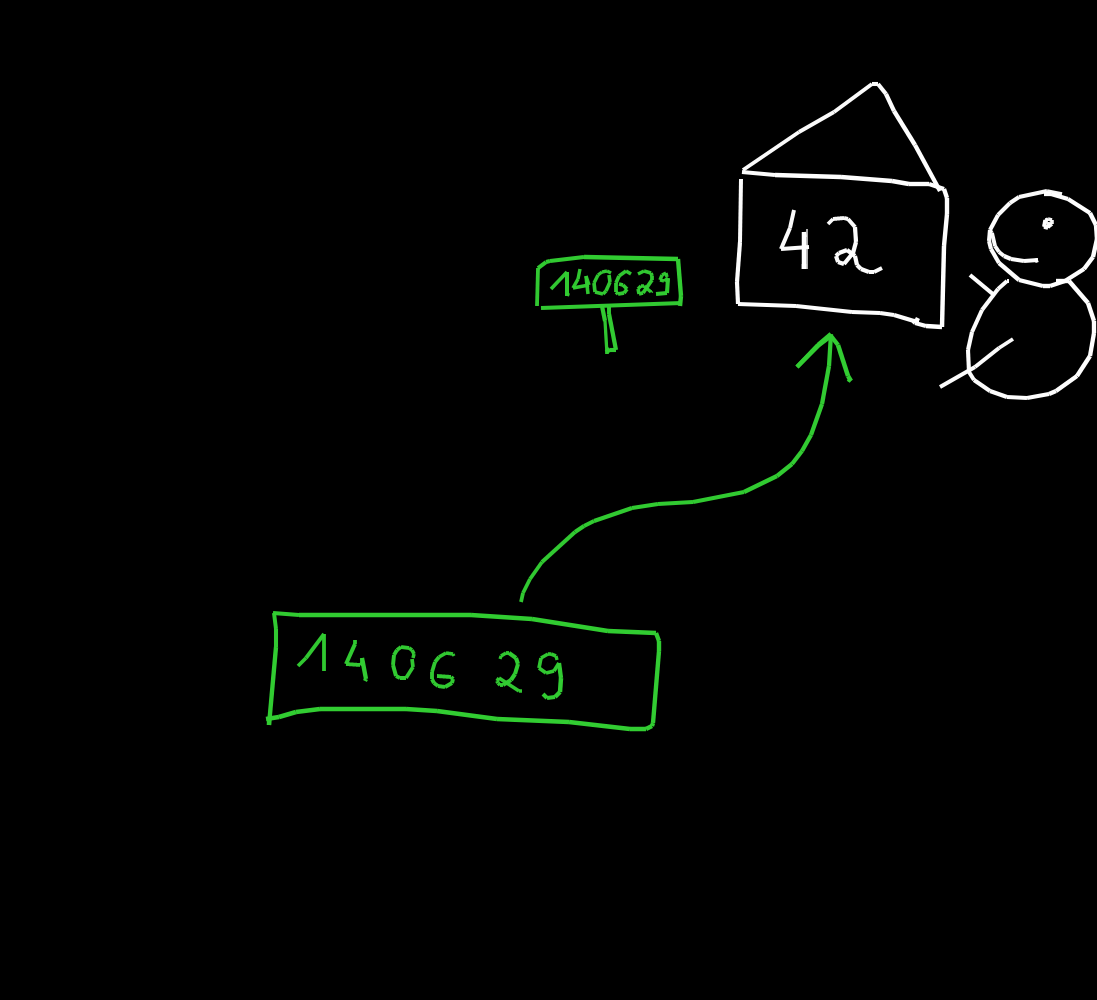
In Python, when numbers are small (between -5 and 255 let say), the memory address are equal.
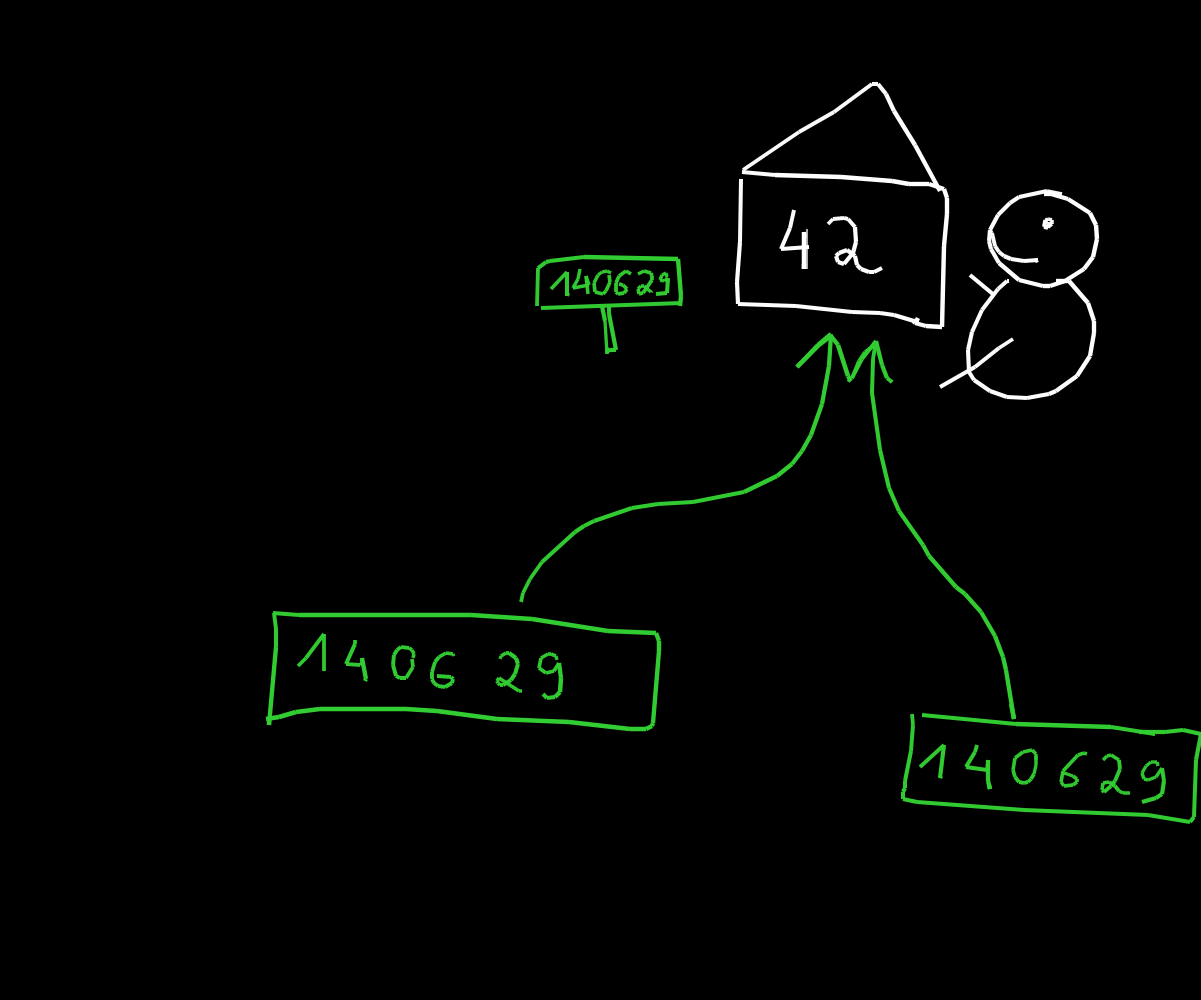
x = 42
y = 42
print(id(x))
print(id(y))
139907129622096
139907129622096
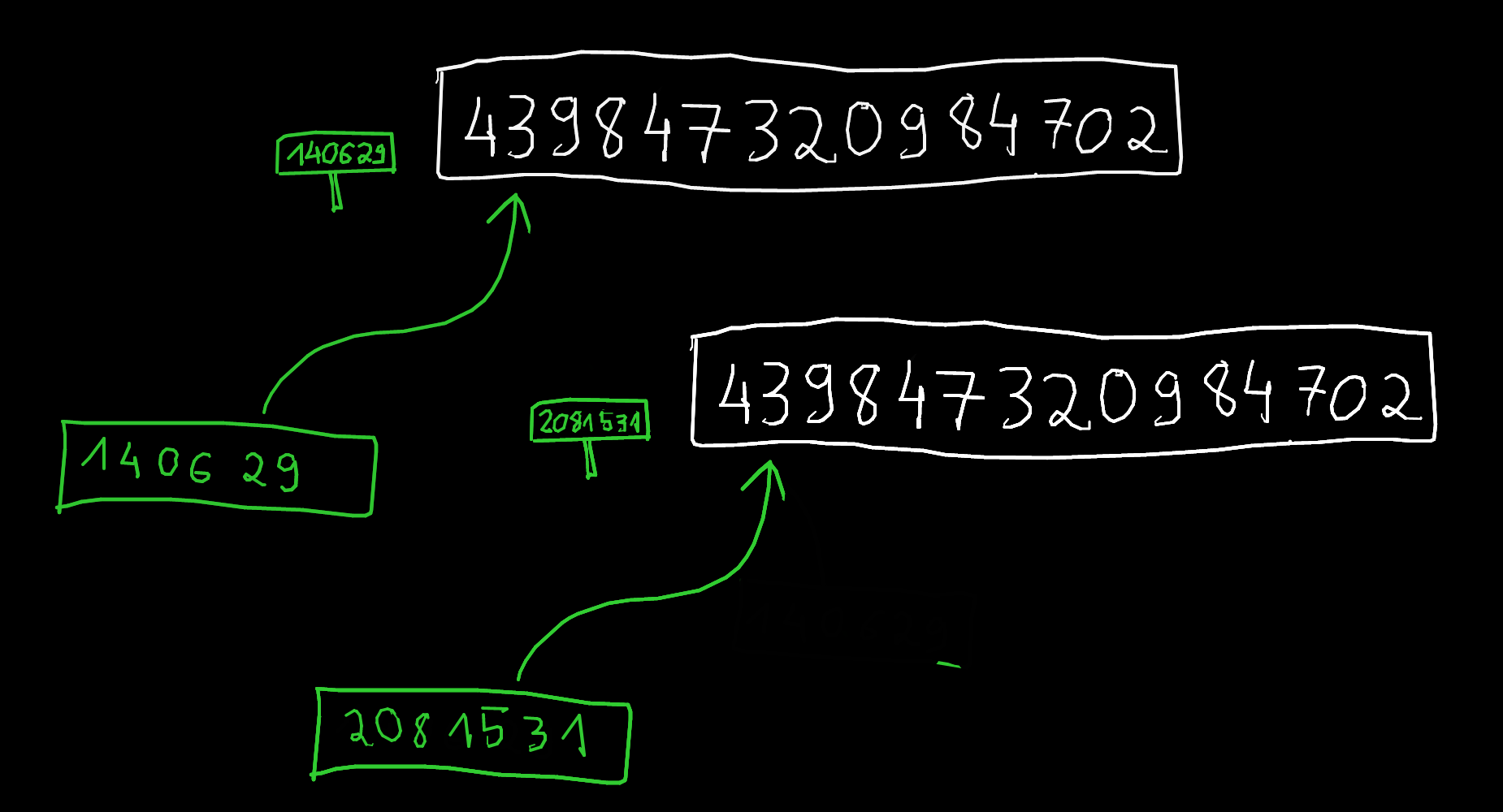
x = 4398473209847023984723981029836012983
y = 4398473209847023984723981029836012983
print(id(x))
print(id(y))
139906654312272
139906654314288
L = (1, 4)
print(id(L))
139906654305152
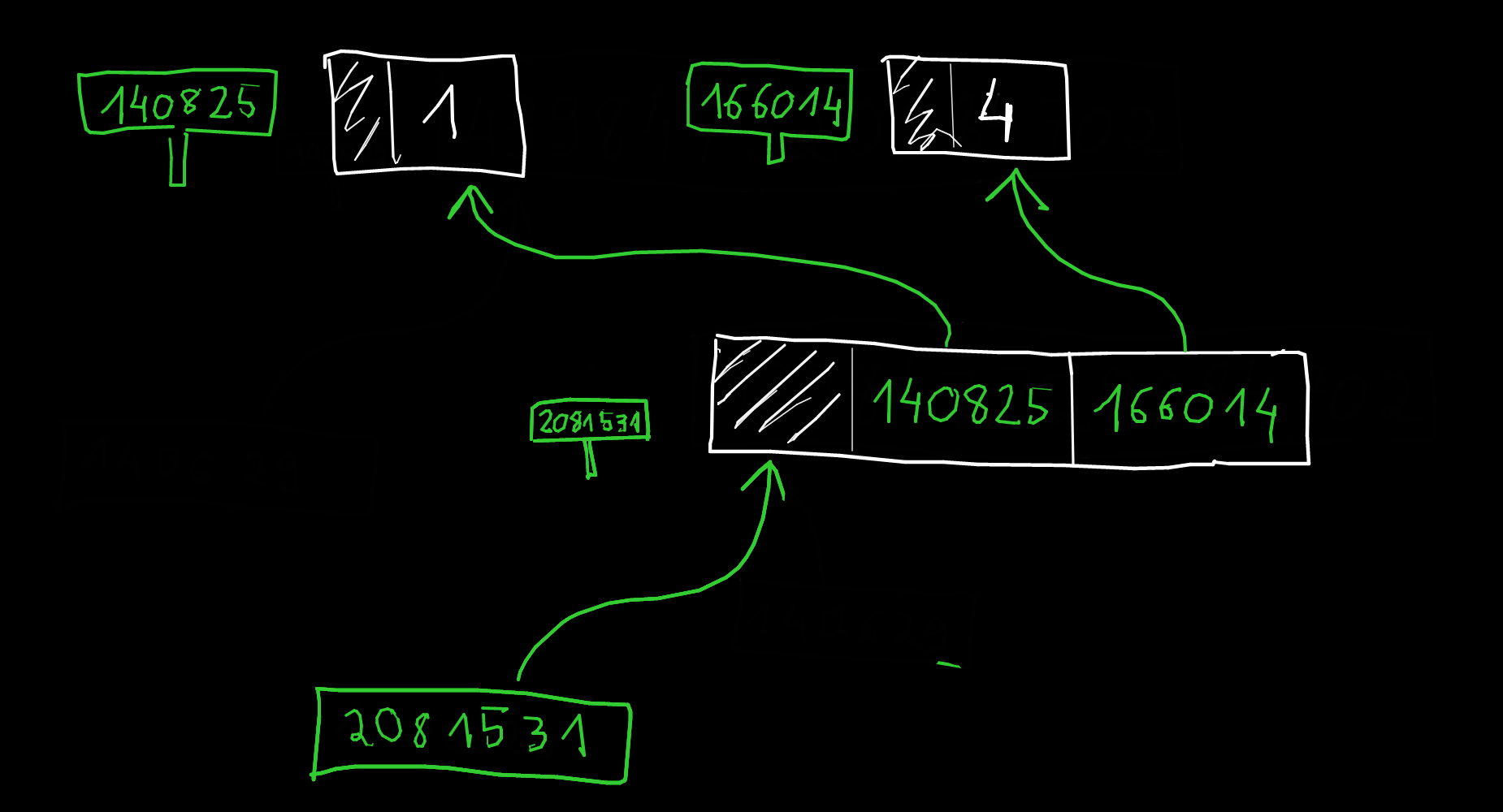
L = (1, 4)
M = (1, 4)
print(id(L))
print(id(M))
139907016431104
139906654343488
Types
Python is dynamically typed: each variable x has a type type(x).
type(2)
int
type([1, 2])
list
type((1, 2))
tuple
type((1,))
tuple
type({1, 2})
set
type(frozenset((1, 2)))
frozenset
Mutability vs Immutability
A variable is mutable when the content can be changed, and immutable otherwise.
| Mutable | Immutable |
|---|---|
int 42, bool True, float 37.5 | |
str "hello" | |
list [1, 2, 3] | tuple (1 2 3) |
dict {"x": 5, "y":2} | from collections import namedtuple |
namedtuple('ImmutableRobot', ['name', 'brandname']) (prefer typing.NamedTuple) | |
| object of a given custom class | |
| set | frozenset |
x = 2
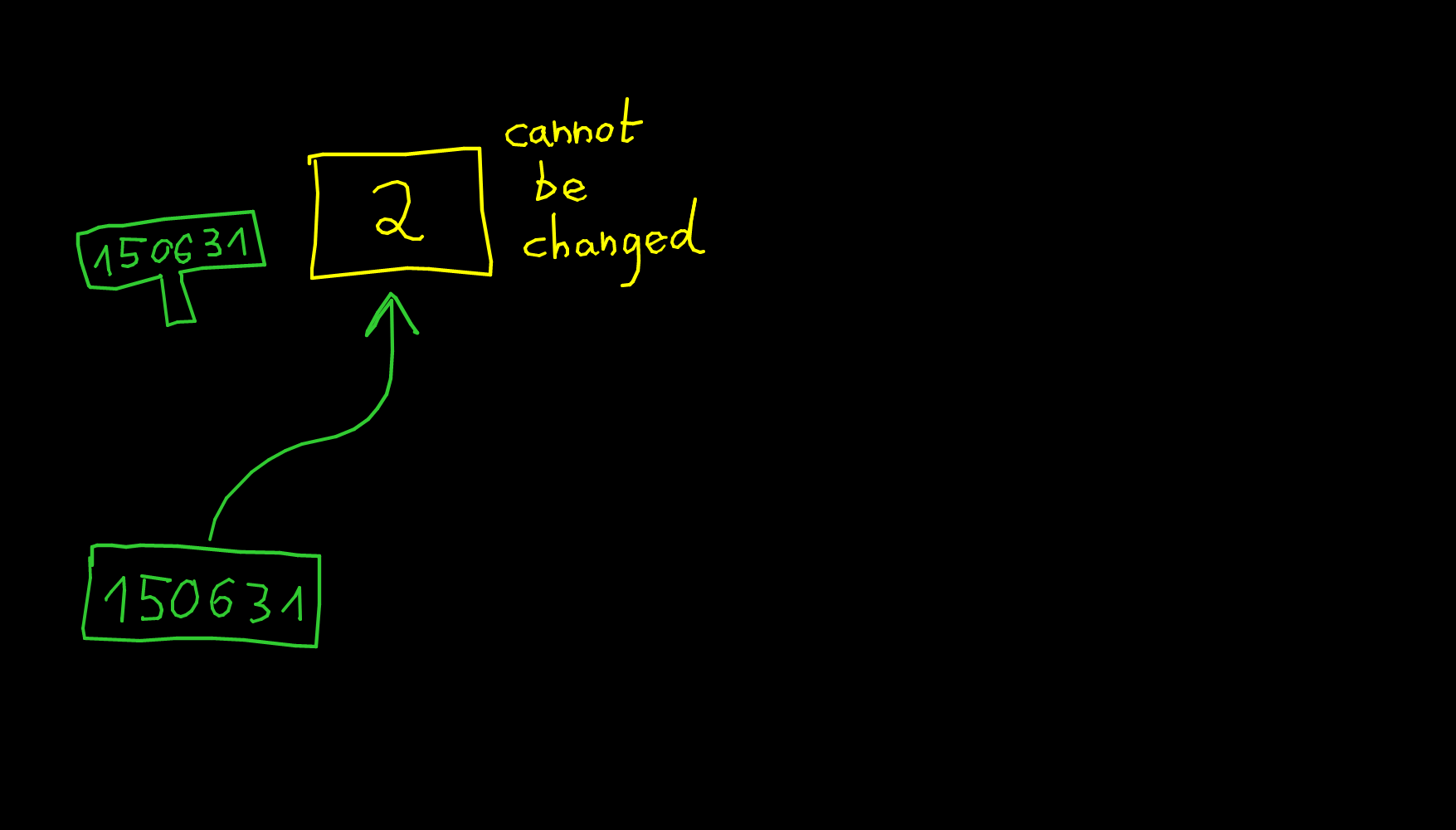
x = 2
x += 1
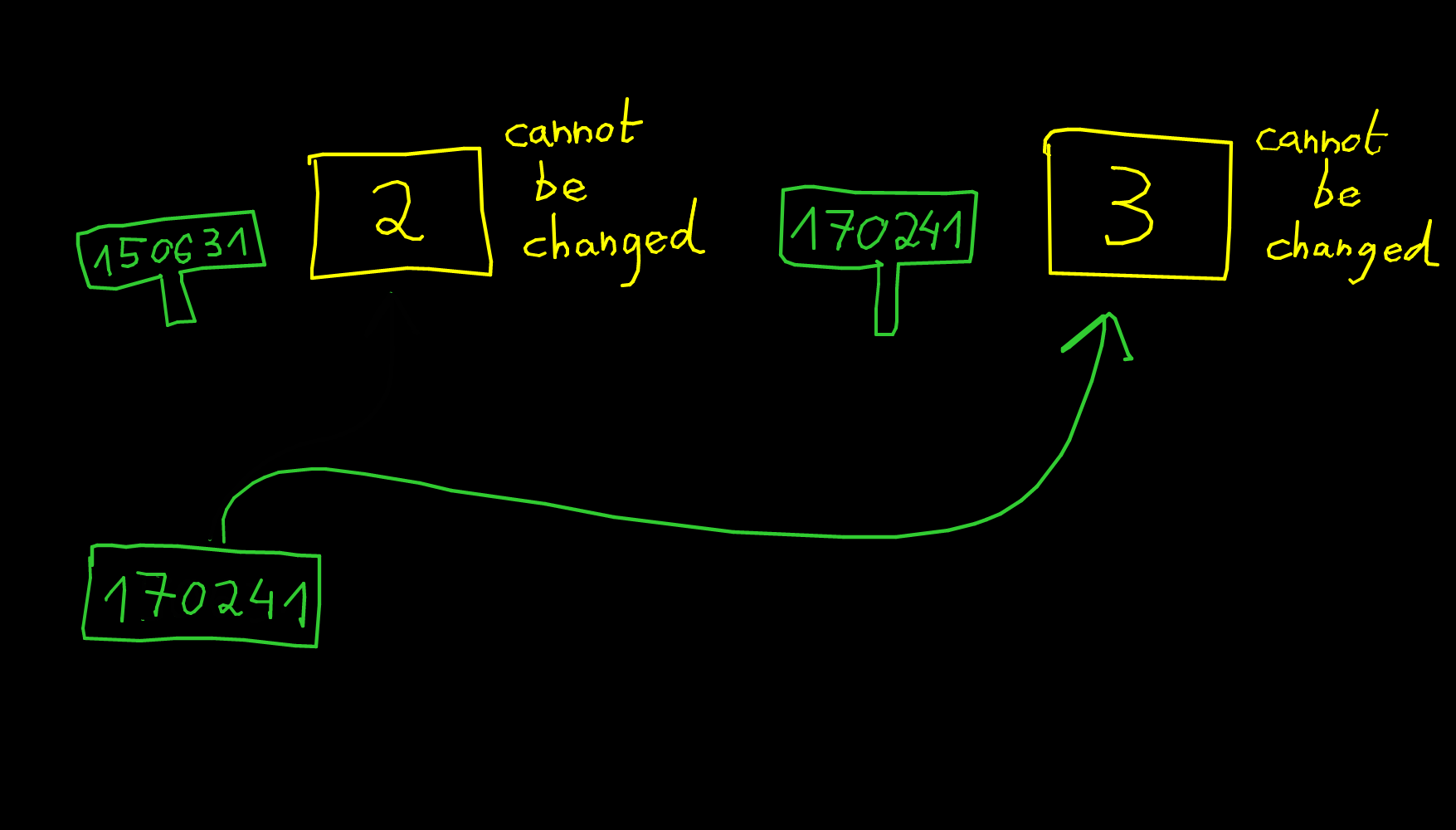
x = (1, 4)
x = (1, 4)
x[0] = 2
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[16], line 2
1 x = (1, 4)
----> 2 x[0] = 2
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
x = [1, 4]
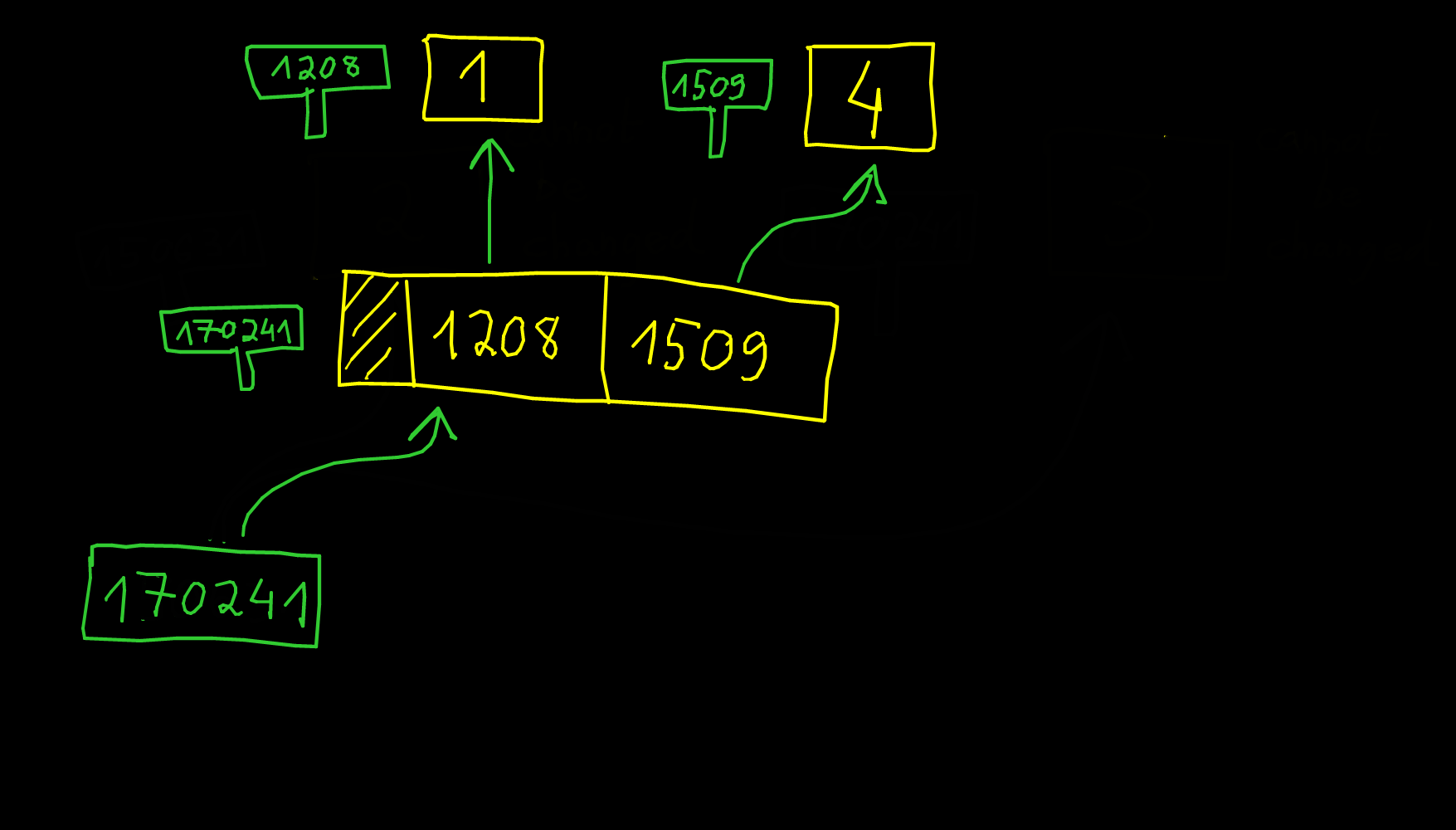
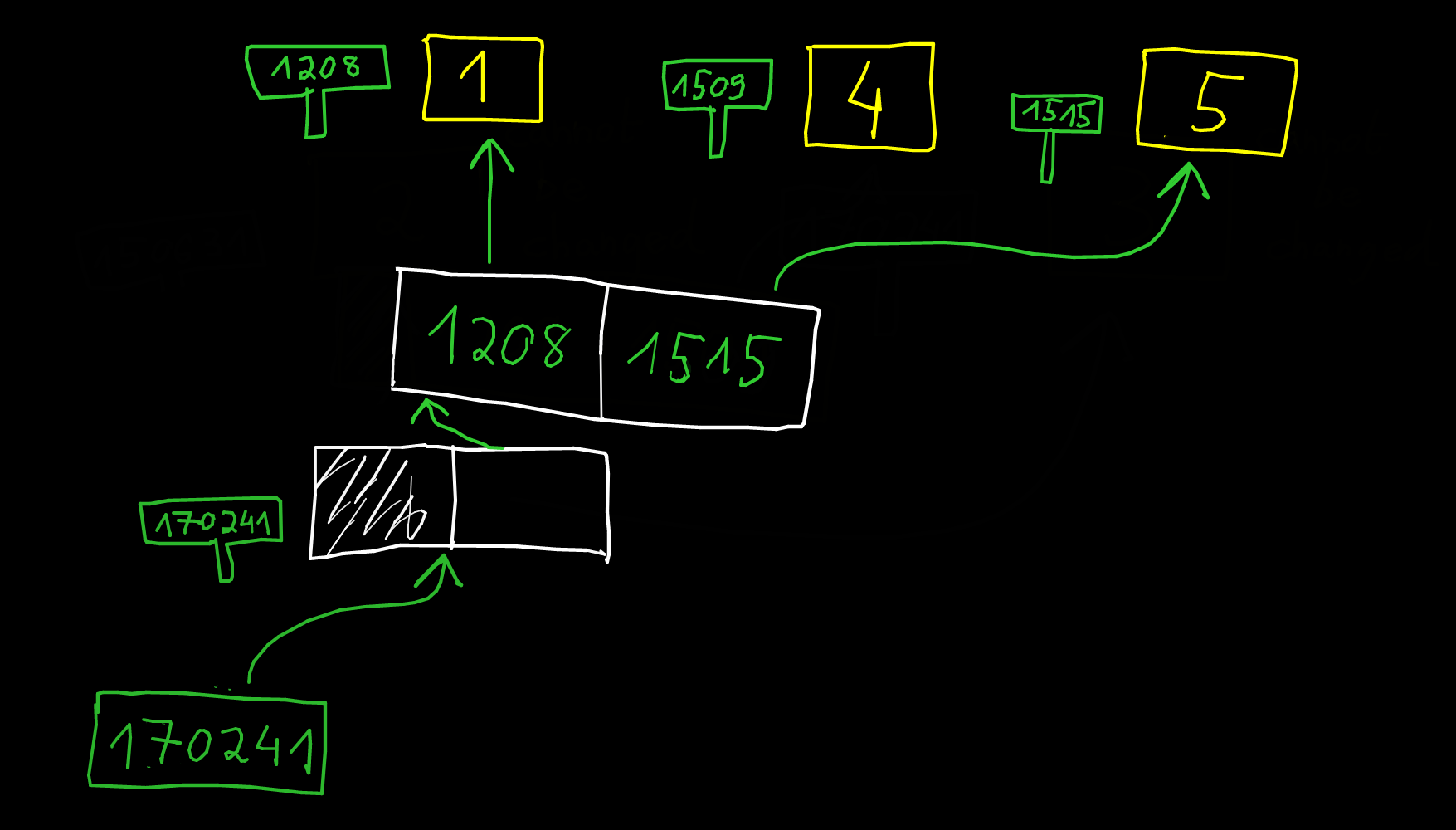
- What do you think about this picture for the datastructure for a list?
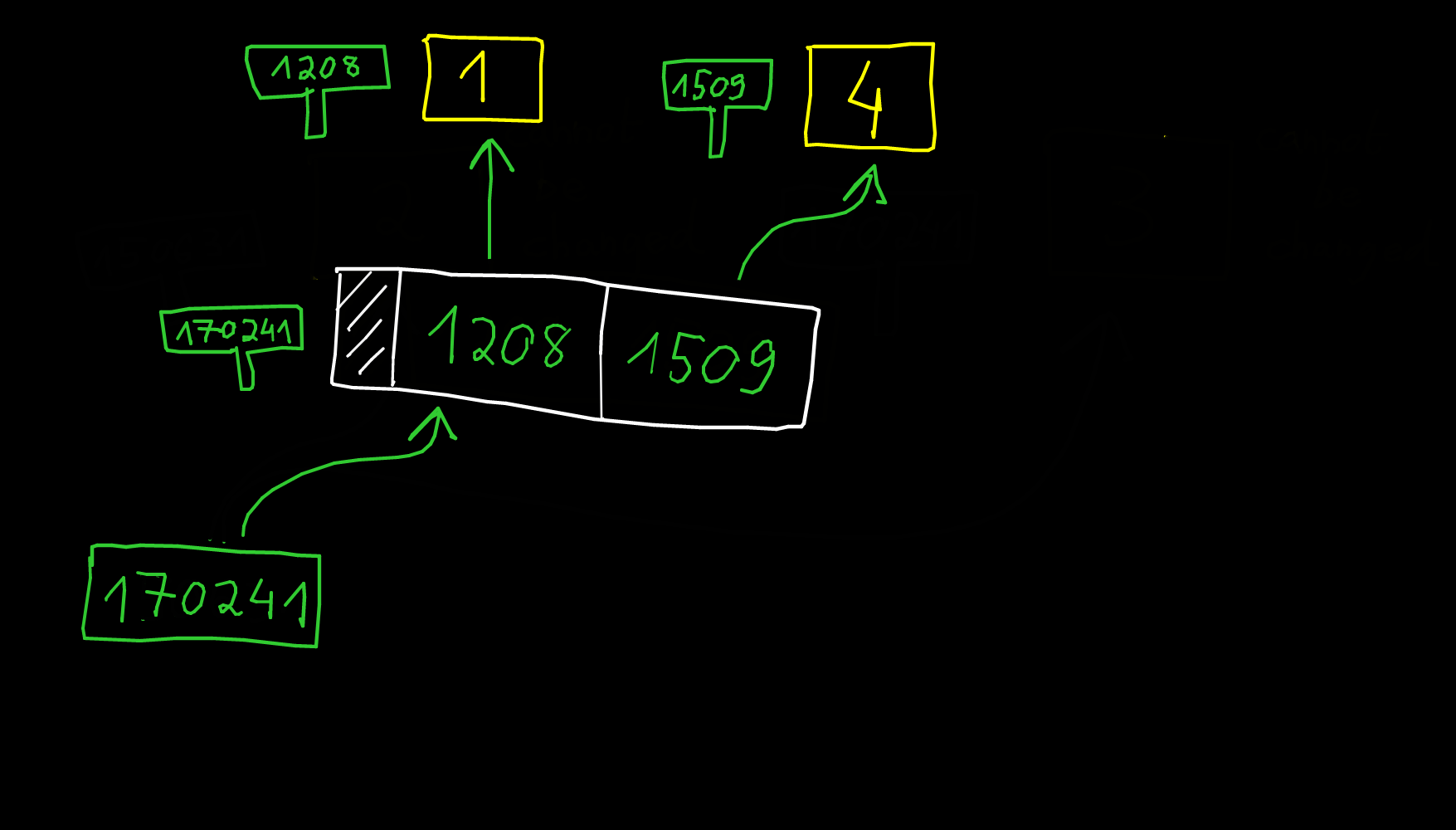
The problem is about resizing the list. The pointer may change. The solution in CPython is to add a new level of indirection.
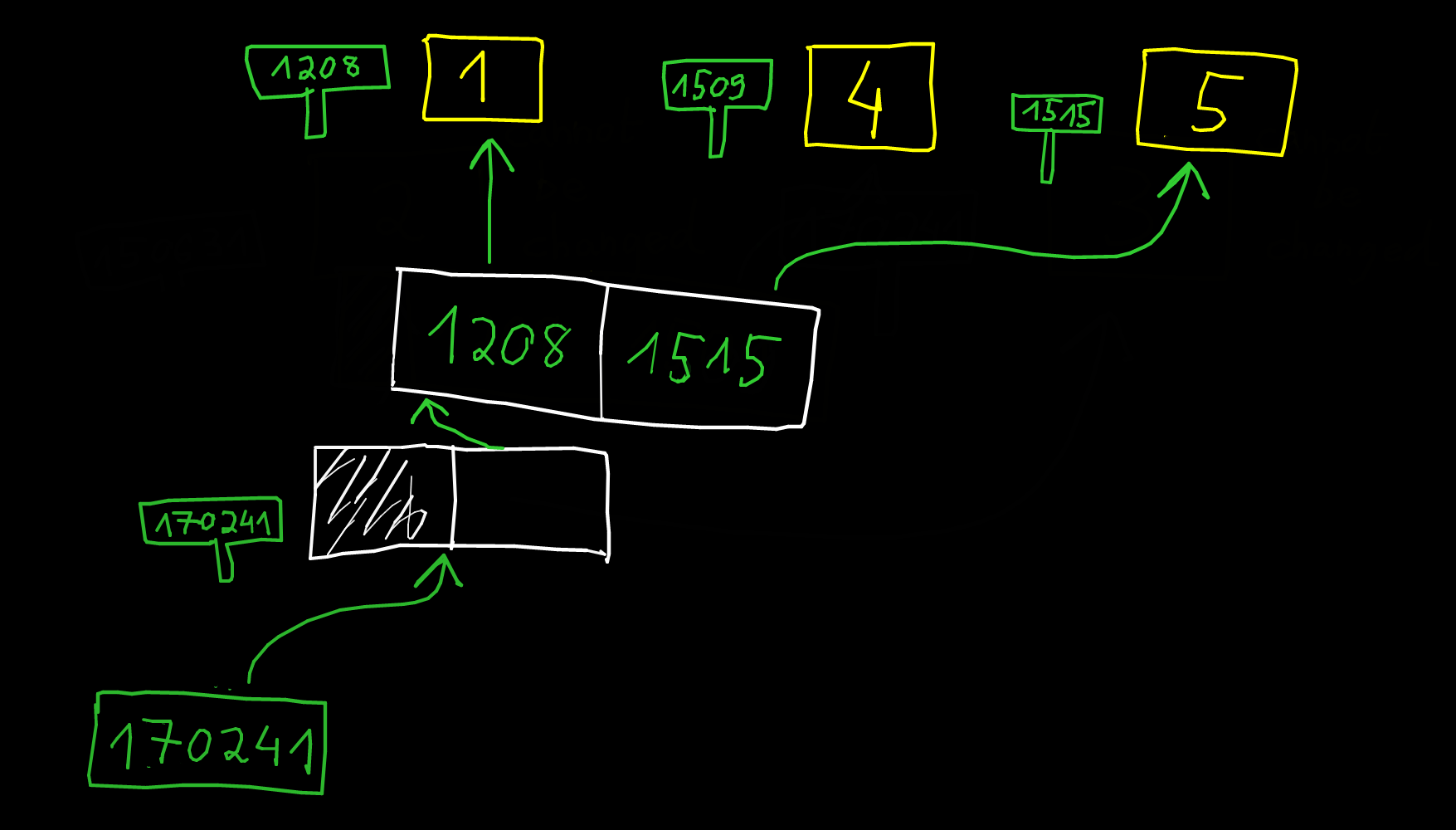
x = [1, 4]
x[1] = 5
Functions
For the function, it is the same.
def f(x):
return x+1
type(f)
function
Attributes and methods
Each type, e.g. int is a class has attributes and methods obtained with dir(int). dir(2) gives attributes and methods of 2.
dir(int)
['__abs__',
'__add__',
'__and__',
'__bool__',
'__ceil__',
'__class__',
'__delattr__',
'__dir__',
'__divmod__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__float__',
'__floor__',
'__floordiv__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__getattribute__',
'__getnewargs__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__index__',
'__init__',
'__init_subclass__',
'__int__',
'__invert__',
'__le__',
'__lshift__',
'__lt__',
'__mod__',
'__mul__',
'__ne__',
'__neg__',
'__new__',
'__or__',
'__pos__',
'__pow__',
'__radd__',
'__rand__',
'__rdivmod__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__rfloordiv__',
'__rlshift__',
'__rmod__',
'__rmul__',
'__ror__',
'__round__',
'__rpow__',
'__rrshift__',
'__rshift__',
'__rsub__',
'__rtruediv__',
'__rxor__',
'__setattr__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__sub__',
'__subclasshook__',
'__truediv__',
'__trunc__',
'__xor__',
'as_integer_ratio',
'bit_length',
'conjugate',
'denominator',
'from_bytes',
'imag',
'numerator',
'real',
'to_bytes']
dir(2)
['__abs__',
'__add__',
'__and__',
'__bool__',
'__ceil__',
'__class__',
'__delattr__',
'__dir__',
'__divmod__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__float__',
'__floor__',
'__floordiv__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__getattribute__',
'__getnewargs__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__index__',
'__init__',
'__init_subclass__',
'__int__',
'__invert__',
'__le__',
'__lshift__',
'__lt__',
'__mod__',
'__mul__',
'__ne__',
'__neg__',
'__new__',
'__or__',
'__pos__',
'__pow__',
'__radd__',
'__rand__',
'__rdivmod__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__rfloordiv__',
'__rlshift__',
'__rmod__',
'__rmul__',
'__ror__',
'__round__',
'__rpow__',
'__rrshift__',
'__rshift__',
'__rsub__',
'__rtruediv__',
'__rxor__',
'__setattr__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__sub__',
'__subclasshook__',
'__truediv__',
'__trunc__',
'__xor__',
'as_integer_ratio',
'bit_length',
'conjugate',
'denominator',
'from_bytes',
'imag',
'numerator',
'real',
'to_bytes']
dir(f)
['__annotations__',
'__call__',
'__class__',
'__closure__',
'__code__',
'__defaults__',
'__delattr__',
'__dict__',
'__dir__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__get__',
'__getattribute__',
'__globals__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__init__',
'__init_subclass__',
'__kwdefaults__',
'__le__',
'__lt__',
'__module__',
'__name__',
'__ne__',
'__new__',
'__qualname__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__setattr__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__subclasshook__']
f.__code__
<code object f at 0x7f3ea9d110e0, file "/tmp/ipykernel_100995/1304018138.py", line 1>
Reference counters
import sys
lst = []
extra_ref = lst
sys.getrefcount(lst)
3
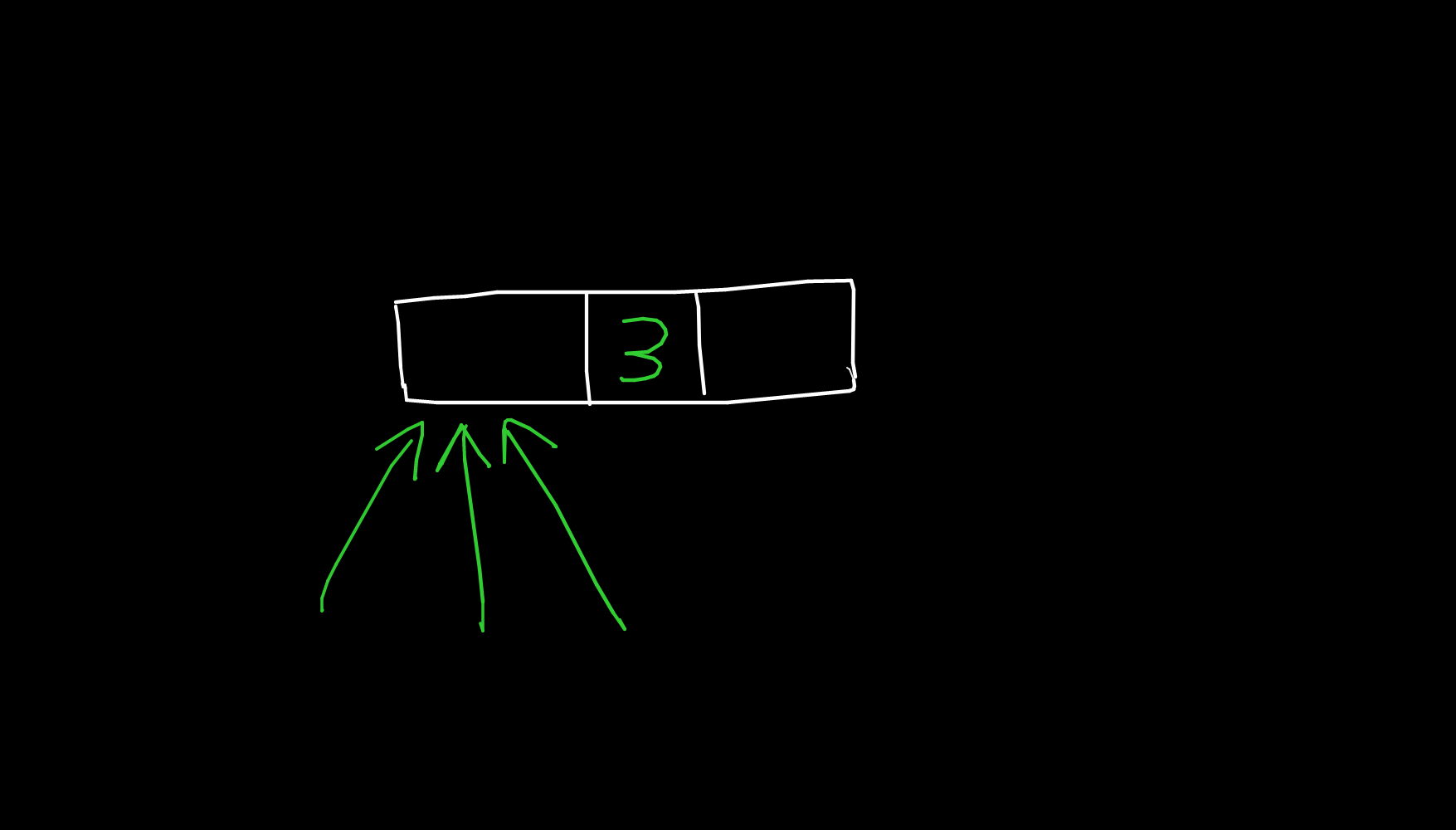
import sys
sys.getrefcount([])
Quiz: same object or not?
L = [[] for i in range(5)]
L[0].append(1)
L
[[1], [], [], [], []]
L = [[]] * 5
L[0].append(1)
L
[[1], [1], [1], [1], [1]]